In today’s business landscape, sustainability has become a core objective for companies. As a B2B buyer in the plant pot industry, understanding whether the products you invest in are biodegradable will significantly impact your procurement decisions, customer satisfaction, and brand image. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the biodegradability of plant pots, focusing on ceramic and terracotta pots, comparing them with other common biodegradable materials, and offering professional advice for bulk purchases.
1. What Are Biodegradable Plant Pots?
Biodegradable plant pots refer to pots that can break down through microbial action under natural conditions, eventually converting into harmless natural elements such as water, carbon dioxide, and organic matter. These pots don’t leave long-term pollutants in the environment, making them increasingly popular as environmentally friendly products. However, different materials vary significantly in terms of their biodegradation time and process.
2. Are Ceramic and Terracotta Pots Biodegradable?
Many people assume that ceramic and terracotta pots, being highly durable, might not fit the “biodegradable” category. However, these materials are made from natural elements and do possess biodegradability under certain conditions.
Ceramic Pots
Ceramic pots are made from natural clay, fired at high temperatures to create a solid structure. While ceramics are very durable and slow to break down, their natural composition means that over hundreds or even thousands of years, they will gradually degrade into minerals and soil. This slow degradation process categorizes ceramic pots as biodegradable, but they decompose much more slowly than other compostable materials like coir or peat pots.
Terracotta Pots
Terracotta, or clay, is made from natural clay fired at lower temperatures. Compared to ceramics, terracotta is more porous and absorbs moisture, which makes it a popular choice for plant growth and environmental protection. Terracotta degrades more quickly than ceramics, especially in wet soil conditions, breaking down into natural soil over time. This makes terracotta a relatively more biodegradable pot material, ideal for buyers focused on eco-friendliness.

3. Comparison of Biodegradable Plant Pot Materials
In addition to ceramic and terracotta, there are many other biodegradable materials on the market, each with its unique characteristics and environmental impacts. Below is a comparison of common biodegradable materials:
| Material | Decomposition Time | Environmental Impact | Cost Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Hundreds of years | Natural material, decomposes into minerals | High, due to complex manufacturing |
| Terracotta | Decades to centuries | Natural material, gradually degrades into soil | Moderate, widely used and affordable |
| Coir Fiber | 6-12 months | Fully compostable, renewable | Moderate to high |
| Peat | 6-12 months | Limited resource, high demand | Low to moderate |
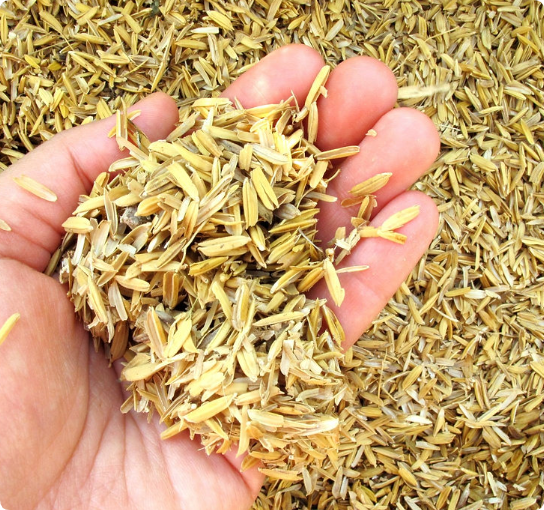
| Rice Hull | 6-18 months | Agricultural byproduct | Low |
| Wood Fiber | 12-24 months | Renewable, compostable | Moderate |
| Compostable Plastics | 12-36 months | Requires industrial composting | Moderate to high |
4. Advantages and Challenges of Ceramic and Terracotta Pots
Advantages of Ceramic Pots
- Aesthetic and Durability: Ceramic pots are widely used in high-end gardening and decorative markets due to their elegant appearance and long-lasting durability. They perform well both indoors and outdoors, resisting most environmental and weather wear.
- Eco-Friendly: Although slow to degrade, ceramic pots contain no harmful chemicals and will eventually return to the earth, making them a sustainable material.
Challenges of Ceramic Pots
- Slow Decomposition: For buyers seeking materials that decompose quickly, ceramic pots might not be the best option. Their breakdown takes significantly longer than other compostable materials.
- High Cost: Due to the complex manufacturing process, ceramic pots tend to be more expensive. This can affect the budget for bulk purchases.
Advantages of Terracotta Pots
- Faster Weathering: Compared to ceramics, terracotta pots degrade much faster, especially in moist environments, making them a quicker biodegradable choice.
- High Breathability: The porous nature of terracotta allows air circulation in the soil, which helps plants grow healthier.
Challenges of Terracotta Pots
- Fragility: Terracotta pots are more fragile than ceramic ones, which means they can be easily damaged during transport and handling, requiring extra care.
- High Absorption: While the absorbency of terracotta helps keep plants hydrated, in dry climates, it may cause soil to dry out too quickly.
5. Market Prospects for Biodegradable Plant Pots
As the global demand for sustainable products increases, biodegradable pots are rapidly becoming a popular choice for buyers. Although ceramic and terracotta pots decompose more slowly, they remain important in the eco-friendly market due to their natural composition and environmental benefits. For B2B buyers, the durability and eco-friendliness of ceramic and terracotta pots make them ideal for long-term gardening and decorative projects.
However, for those looking for quicker-degrading options, materials like coir fiber, peat, or rice hull pots may be more suitable. Buyers should choose materials flexibly based on their customer needs, market trends, and project requirements.
6. Recommendations for Purchasing Biodegradable Plant Pots
When purchasing biodegradable plant pots, B2B buyers should consider the following factors:
- Product Use: If you need long-lasting, durable pots, ceramic and terracotta pots are great choices. If you need fast-degrading materials, coir fiber or rice hull pots may be more suitable.
- Cost Efficiency: Although ceramic pots may be more expensive, their long-term durability could save you from frequent replacements. Terracotta pots offer moderate costs, ideal for bulk purchases.
- Market Demand: Understand your customers’ preferences and sustainability goals to ensure the products you source meet their expectations for eco-friendliness.
- Environmental Certification: Opt for products that meet international environmental certifications, such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) or European Bioplastics Certification, to enhance your product’s competitiveness in the green market.
7. Conclusion: Biodegradability of Ceramic and Terracotta Pots and Future Trends
Although ceramic and terracotta pots take a longer time to degrade, they are still biodegradable and environmentally friendly materials. They are particularly suited for projects requiring durability and aesthetics. In the future, as the demand for sustainable products continues to grow, ceramic and terracotta pots will remain important in eco-conscious gardening and indoor-outdoor decor markets.
When sourcing biodegradable plant pots, B2B buyers must consider not only the degradation speed of the materials but also their durability, market demand, and overall cost-efficiency. By making the right material choices and procurement strategies, you can meet sustainability goals while improving business efficiency and customer satisfaction.
At HalePlanter, we offer a wide range of sustainable plant pots, including ceramic, terracotta, and other natural biodegradable products. Whatever your project needs, we are committed to helping you find the best eco-friendly plant pot solutions. Contact us to learn more about how we can help you source the highest quality plant pots for your business.
HalePlanter is a leading supplier of ceramic and biodegradable plant pots, serving B2B buyers worldwide. We provide customized solutions and prioritize sustainability across all aspects of our business.



















